| বাংলায় পড়ুন | Researchers and Reporters: Shama Sultana Isfaqul Kabir |
Natural resources abound on the African continent. Iron, copper, cobalt, gold, diamonds, and many other precious natural resources are among the many rich mineral resources found on this continent. Modern technology like your laptop, cell phone, and other electrical gadgets, as well as the current generation of electric cars, are made using them. The biggest technology corporations in the world rely on these African mines. Chinese corporations’ impact on Africa’s mining industry has been growing daily in recent years. In addition to its economic dominance, China also has geopolitical power over Africa. But why are Chinese companies in charge of Africa’s mining industry?
- China’s mineral demand and Africa’s role
One of the economies with the quickest rates of growth in the world is China. Africa provides China with a variety of mineral substances, including cobalt for batteries used in electric vehicles and cell phones, copper for electrical gadgets, and iron for the creation of steel. Approximately 60% of the world’s cobalt supply is controlled by China, and the Congo is a major supplier of this metal.
Even though Africa has an abundance of mineral resources, its lack of comparatively sophisticated technology and robust economic infrastructure causes it to lag in the extraction and processing of its resources. Chinese corporations have seized the opportunity. They have made significant investments and used modern technologies to establish a prominent position in Africa’s mining industry.
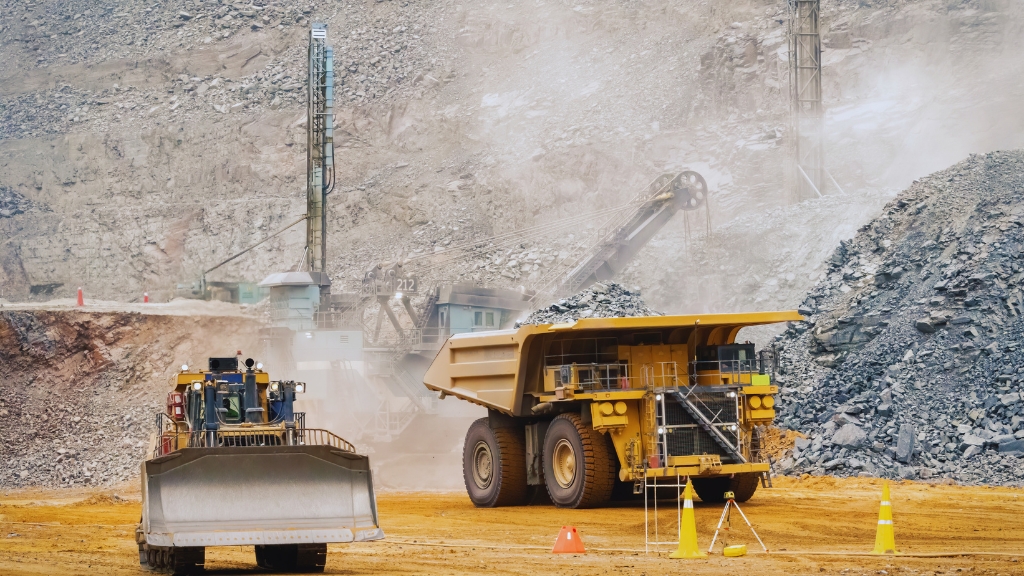

- Chinese investment strategy: infrastructure development and debt diplomacy
Chinese companies have focused on infrastructural development in Africa in addition to mining. Through long-term partnerships with African governments, the Chinese government and enterprises are constructing seaports, highways, electricity supply systems, and railroads in a number of African nations. By making billions of dollars in investments, Chinese businesses in the Congo have won the government’s trust. Through this, the Congolese government has entered into an agreement with Chinese companies whereby the Chinese companies will have to make significant investments to extract mineral resources, while the Congolese government will receive facilities to build ports, roads, railways, and power systems.
Wang Yi, the Chinese Foreign Minister, stated that “China has become an important partner in Africa’s mining industry.” However, Zhao Changpeng, a former Chinese ambassador to the Congo, contended that “China’s involvement in the mining sector is not just a business interest, but part of a larger development partnership with African countries.”
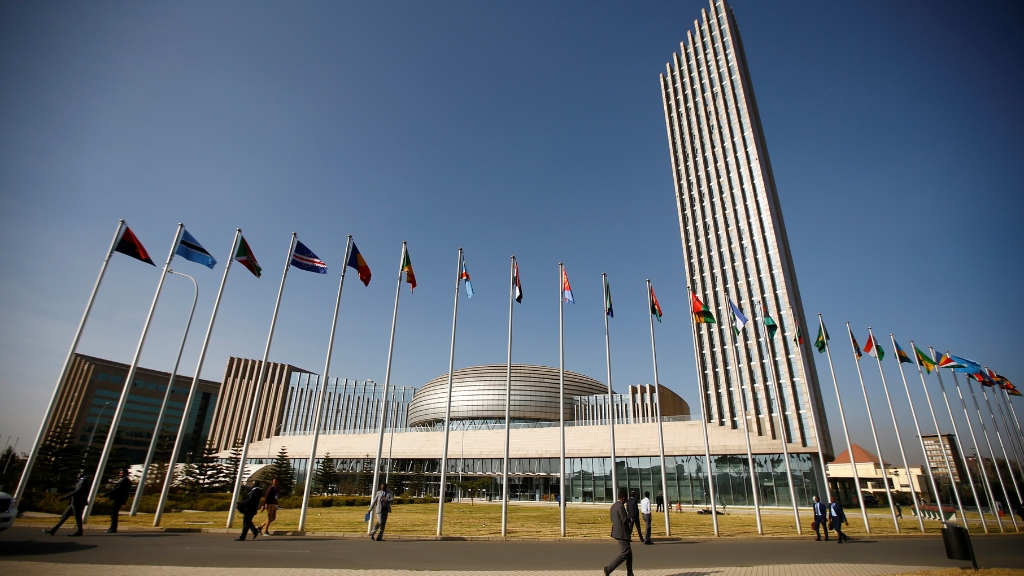

- Low labor costs and lower production costs
Workers are accessible in most African countries for very little money because they are generally impoverished. In order to further their interests, Chinese businesses are utilizing this chance. Modern technology has greatly facilitated the extraction of mineral resources by Chinese corporations. Workers in mines under Chinese administration are subjected to far worse working conditions, which is causing controversy. Workers from those mines are frequently reported dead.
- Political Relations and Influence
African nations and China have established close political and economic ties. China and African nations have developed close ties through the employment of diplomatic means. Dealing with African nations is a simple way for Chinese businesses to operate. A $200 million donation from China helped construct the African Union’s headquarters. China is enhancing its economic and political relationships with African nations in part through this donation. China’s “Belt and Road Initiative” is exemplified by this infrastructural development across Africa, while some critics think it is a tactic to increase China’s influence in the continent.
Additionally, through its “Belt and Road Initiative” (BRI) initiatives, China has been lending huge sums of money to an array of African nations. Chinese companies have frequently received preferential treatment in the African mining sector as a condition of repaying the loans.
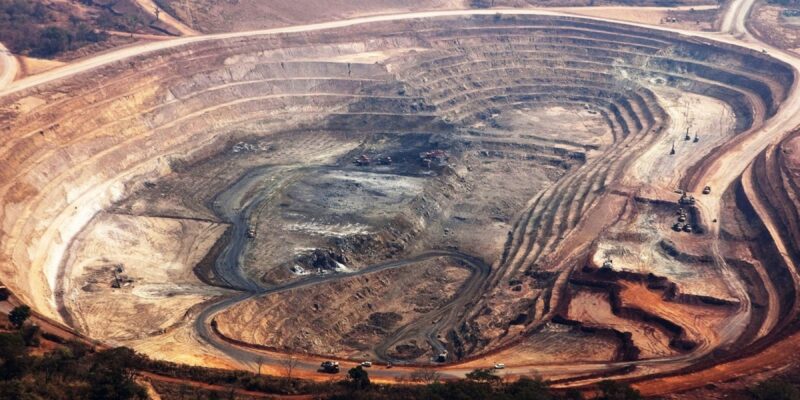
- Impacts on the Environment and Society: Prospects and Difficulties
African local groups have responded differently to Chinese corporations’ mineral mining operations. The growth of Africa’s human resources industry is, on the one hand, creating jobs and economic expansion. However, environmental harm, pervasive cultural effects, and resource overuse have led to numerous disputes among nations. The mining of cobalt in Congo is damaging local agricultural fields and polluting the environment as a result of the actions of Chinese companies.
China’s hegemony in Africa’s mining industry is a complicated and multifaceted problem. It has a tight connection to China’s political clout, investment plans, and economic demands. African progress is being facilitated by this domination, but it also brings with it issues like ecological damage, dependency, and foreign control over domestic resources. African nations need to manage their resources in a long-term manner. To maximize the benefits of this supremacy and reduce the drawbacks, they must implement effective governance and equitable trade agreements.























Comments